WHAT IS RESPIRATORY SYSTEM? BMLT
The respiratory system (also respiratory apparatus, ventilatory system) is a biological system, consisting of specific organs and structures used for gas exchange in human.
- Organs of Respiratory System:
- Nose and nasal cavity.
- Pharynx
- Larynx
- Trachea
- Two bronchi
- Bronchioles
- Two Lungs
NOSE AND NASAL CAVITY
POSITION AND STRUCTURE Main route of air entry.
Two cavities divided by a SEPTUM. Anteriorly consist hyaline cartilage. The roof is formed by ethmoid bone
The floor is formed by roof of the mouth. The medial wall formed by the septum.
The lateral wall formed by the maxilla.
RESPIRATORY FUNCTIONS OF THE NOSE
- The first of the respiratory passages.
- Warming-
Due to the immense vascularity of the mucosa.
This occurs due to hairs which trap larger particles.
As air travels over the moist mucosa,it becomes saturated with water vapour.
PHARYNX
The pharynx is the part of the throat that is behind the mouth and nasal cavity and above the esophagus and the larynx.
Length- 12-14cm (extends from the base of the skull to the level of 6th cervical vertebra.)
Position
Superiorly-Base of the skull.
Inferiorly-Continuous with the oesophagus.
Anteriorly-Incomplete wall because of the nose,mouth and larynx opening.
Posteriorly-Areolar tissue & first 6 vertebra.
For descriptive purposes the pharynx is divided into three parts:
(i)The nasopharynx
(ii)The oropharynx
(iii) The laryngopharynx
(i) The nasopharynx
The nasal part of the pharynx lies behind the nose.
(ii)The oropharynx
The oral part of the pharynx lies behind the mouth.
(iii) The laryngopharynx
The laryngeal part of the pharynx extends from the oropharynx.
STRUCTURE
The pharynx is composed of three layers: Mucous membrane lining
Fibrous tissue Smooth muscle
Blood supply
Facial artery Facial vein
Internal jugular veins
Nerve supply
Vagus nerve Glossopharyngeal nerve
Functions
- Passageway for air and food.
- Warming and humidifying.
- Taste.
- There are olfactory nerve endings.
- Hearing.
- The auditory tube,extending from the nasopharynx to each middle ear.
- Protection.
- The lymphatic tissue of the pharyngeal tonsils produces antibodies.
- Speech.
- Act as a resonating chamber for sound ascending from the larynx.
LARYNX
- POSITION
- The larynx or voice box extends from the root of the tongue.
- It lies in front of the laryngopharynx at the level of 3rd , 4th ,5th and 6th cervical vertebra.
- Until the puberty there is little difference in the size of the larynx between the sexes.
- It grows larger in the male.
Superiorly-The hyoid bone & roof of the tongue.
Inferiorly-Continuous with the trachea.
Anteriorly-The muscle of the neck.
Posteriorly-.The laryngopharynx and 3rd to 6th cervical vertebra.
STRUCTURE
The larynx is composed of several irregularly shaped cartilages attached to each other by ligaments and membranes.
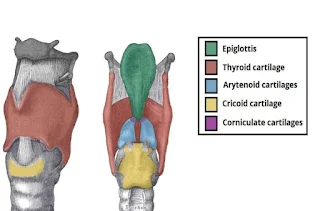
The thyroid cartilage
This is the most prominent & consists of 2 flat pieces of hyaline cartilage & fused anteriorly forming the Adam’s apple.
The cricoid cartilage
This lies below the thyroid cartilage & composed of hyaline cartilage.
The arytenoid cartilages
These are two roughly pyramid-shaped hyaline cartilages situated on top of the broad part of the cricoid cartilage.
This is a leaf-shaped fibroelastic cartilage attached to the inner surface of the anterior wall of the thyroid cartilage.
Superior and inferior laryngeal arteries.
Thyroid veins.
Superior laryngeal nerves.
FUNCTIONS
- Production of sound
- Speech
- Protection of the lower respiratory tract During swallowing the larynx moves upwards and hinged epiglottis closes over the larynx.
- Passageway for air
- Humidifying
- Filtering
- Warming
TRACHEA
Position
The trachea or windpipe is a continuation of the larynx & extends downwards to about the level of T-5 where it divides into right & left primary bronchi.
Superiorly-the larynx
Inferiorly-the right & left bronchi
Anteriorly-upper part-the thyroid gland.
lower part-the arch of aorta & the sternum.
Posteriorly-.the oesophagus
Laterally- the lungs
STRUCTURE
Composed of 3 layers of tissue.
(i) fibrous & elastic tissue
(ii) smooth muscle
(iii) ciliated columnar epithelium
Held open by between 16-20 incomplete cartilage rings (C-shaped)
Blood supply
Inferior thyroid artery Bronchial artery Venous drainage
Inferior thyroid veins
Nerve supply
Laryngeal nerve
FUNCTIONS
- Support and patency
- Mucociliary escalator
- Cough reflex
- Warming
- Humidifying
- Filtering
BRONCHI & BRONCHIOLES
The two primary bronchi when the trachea divides about the level of T-5.
The right bronchus
This is wider,shorter and more vertical than the left bronchus.
Length-2.5cm
After entering the right lung,it divides into 3 branches,one to each lobe.
The left bronchus
This is narrower than the right
Length-5cm
After entering the left lung,it divides into 2 branches,one to each lobe.
STRUCTURE
The bronchi are composed of the same issues as the trachea.
Are lined with ciliated columnar epithelium.











Comments
Post a Comment
Thanks to Come on Comment section